According to statistics, every third man of working age suffers from prostatitis at various stages of life. Constant pain, impotence, infertility - this is not a complete list of problems that threaten patients without treatment. Due to the high urgency and danger of the disease, its symptoms and first manifestations should be known to every man. In this article, you will learn about all the signs and diagnostic methods that can be used to detect prostatitis.
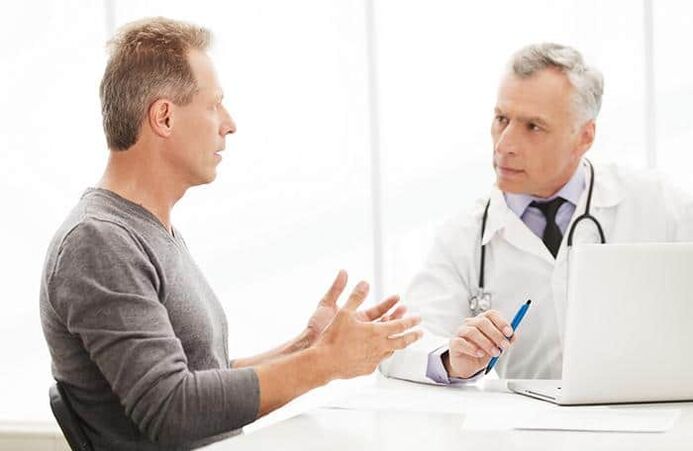

The clinical picture in the initial stages of development
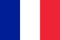
Prostatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the male prostate. A distinction is made between the following forms of disease: acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic pelvic pain syndrome, asymptomatic prostatitis. Each form manifests in different ways, has distinctive signs and features of the course.
It is difficult to say how the disease will play out in every single man. The presence of certain characters depends on a number of external and internal factors. To facilitate the characterization of the pathology, it is customary to divide all symptoms of prostatitis into three large groups: those associated with urinary tract disease, sexual dysfunction and mental health problems. The first and main symptoms of prostatitis (with the exception of the asymptomatic form) can be the following signs in a man:
- Pain in the pelvis, back, groin.
- Pain and burning sensation when urinating.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Feeling that your bladder is not completely emptied and you have an incorrect urge to urinate.

Pain in the pelvis, back, groin, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, and an incorrect urge to urinate are signs of prostatitis.
The listed symptoms occur due to impaired urinary function, which is due to the anatomical features of the structure and location of the bladder and prostate. Signs of prostatitis related to sexual dysfunction are also significant and pronounced. The most common symptoms of men are:
- Weak erection.
- Quick onset of ejaculation during intercourse.
- Lack of orgasm or decreased sensitivity.
- Pain in the urethra and rectum when ejaculating.
Problems with urination and difficulties in intimate life due to inflammation of the prostate are very annoying to the man. Patients with prostatitis are forced to change their way of life, refuse habits, family relationships become more complicated. Obsession with your problem leads to increased nervousness, anxiety, and decreased libido, which can be described as indirect signs of prostatitis and belong to the third group of symptoms mentioned above (mental disorders).
Prostatitis in men can often be confused with prostate adenoma or cancer, a pathology of the bladder. All of these diseases appear similarly, especially in the early stages. It is very difficult to distinguish them for an unprepared person, so differential diagnosis is made by analyzing all the objective symptoms, laboratory and instrumental research data that are present. Since each form of prostatitis has specific signs and characteristics, it is advisable to consider them separately.
Features of certain forms of the disease
Acute prostatitis is inflammation of the male prostate caused by the entry of an infectious agent into the organ through the blood, lymph, or urethra. The disease begins abruptly and is characterized by the severity of all clinical symptoms. The main symptoms of acute prostatitis:
- The rise in body temperature to 39-40 degrees.
- Symptoms of general poisoning (headache, weakness, fatigue, decreased performance, etc. ).
- Severe pain in the perineum, sacrum, above a man's pubic joint.
- Frequent, painful urination.
- Sometimes men have urinary retention.

The temperature 39-40 is a clear sign of inflammation of the prostate.
Acute inflammation of the prostate usually ends with recovery or chronicity of the process (symptoms can be disruptive for several months). But more often this form of prostatitis is primary and a result of the presence of bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking, etc. ), a sedentary lifestyle, a lack of vitamins and minerals, prolonged sexual abstinence, or a non-prostatitis -aggressive sexually transmitted infection or infectionTaking normal means microflora. The clinical picture of chronic prostatitis looks rather poor in relation to the acute form, the symptoms of the disease are inconsistent, which makes the diagnosis much more difficult. Most typical of the chronic form of prostatitis are the following symptoms:
- Increased need to urinate, including at night.
- Pain when urinating and also when ejaculating.
- Dull pain in the lower back, pelvis, over the bosom, etc.
Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS) in a man combines recurrent pain in the prostate area, temporary disorders of the urinary and reproductive systems. CPPS in medicine is a more comprehensive concept, since the pathology can be pathogenetically based on a tumor or an ischemic process, disorders of the nervous system, and not just inflammation. The inconsistency of the presence of signs of prostatitis in chronic pelvic pain syndrome significantly complicates the diagnosis, but it is much more difficult to perform in an asymptomatic form. In these cases, the data from laboratory and instrument research methods play the most important and crucial role.
Diagnostic techniques
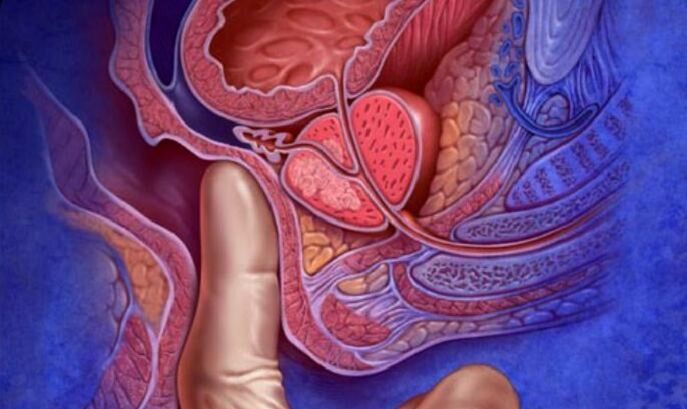
A definitive diagnosis cannot be made based on the symptoms of prostatitis alone. In addition, doctors need to collect medical history: information about when symptoms appeared, their relationship to the most important and important events in life, physical and mental shocks, all possible predisposing factors are clarified, and so on. A physiological exam is always done - a digital rectal exam in the knee-elbow position of a sick man, lying on his side with his legs bent or standing with his body bent forward. During this study, you can find signs that are characteristic of prostatitis (the presence of all is not required):
- Enlargement of the male sex gland.
- The shape of the organ is correct or flattened with a depression.
- Dressed or doughy consistency.
- Smoothness of the boundaries of the prostate.
- Increased pain with pressure.
Further examination of a patient with symptoms of prostatitis is complemented by laboratory methods. General and biochemical blood tests are prescribed - there are no specific changes in indicators, only indirect signs that make it possible to assess the presence of an inflammatory process in a man's body (an increase in the number of leukocytes, acute-phase proteins, accelerated ESR). The results of urine tests will be valuable, which will make it possible to assess the presence of an infectious process in the genital tract and determine the causative agent for starting etiological treatment. In addition, urologists can prescribe an analysis of prostate secretion, a spermogram.
Among the instrumental methods of diagnosing prostate diseases, the most informative is TRUS - transrectal ultrasound. In this case, a special sensor is used, which the doctor inserts into the rectum. This causes discomfort in a sick man, but it is compensated for by the informational content of this method. With the help of TRUS, it is possible to assess the structure of the organ, assess the presence of tissue inflammation, the degree of narrowing of the urinary tract, and exclude the presence of stones. The main echoes of prostatitis: enlargement of the organ, edema, fibrosis, sclerotic tissue changes, coarse-grained and heterogeneous structure.
In addition, patients with symptoms of prostatitis undergo uroflowmetry - a special diagnostic manipulation that measures a man's rate of urination. Based on the data of this study, conclusions can be drawn about the degree of narrowing of the urethra and the activity of the detrusor. Uroflowmetry should not replace TRUS, but rather confirm its findings and signs of existing prostatitis.
The schedule for a diagnostic examination for prostatitis can be expanded if it is indicated in a man. A pelvic can be performed to clarify individual points related to diagnosis, cystoscopy, and CT of the pelvis. In unclear cases, a biopsy is performed to differentiate with tumor processes.
What to do when the first symptoms appear
The biggest and most common mistake many men make when they have signs and symptoms of prostatitis is waiting. Each patient hopes that the uncomfortable symptoms are temporary and will soon go away. Untreated prostatitis is harmful to health and leads to irreversible changes in the body, which are fraught with an impaired erection mechanism, infertility or, worse, malignancy of the process (transition to cancer).
To avoid serious complications, at the first signs of prostatitis, every man should consult a urologist who will prescribe treatment. First of all, men receive etiotropic therapy - anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, measures to strengthen the immune system. No surgery is required without complications. Men who have had prostatitis in the past are at risk and there is a high chance it will recur. Therefore, post-recovery prevention plays a major role.